(i) Multiply both sides of
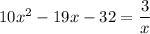
by x and rearrange terms to get
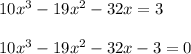
The left side factorizes to
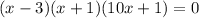
which means x = 3, x = -1, or x = -1/10. We only care about 0 ≤ x ≤ 6, so we take x = 3.
(ii) In the equation
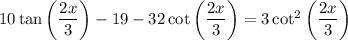
notice that multiplying both sides by
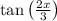 gives the same equation as in (i), but with x swapped out for
gives the same equation as in (i), but with x swapped out for
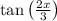 :
:
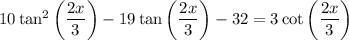
Then it follows that
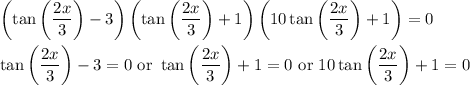
Solve each case individually.
• Case 1:
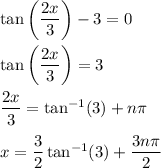
(where n is an integer)
• Case 2:
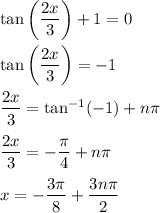
• Case 3:
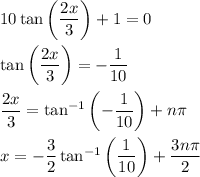
From here, it's a matter of determining for which n we have 0 ≤ x ≤ 6.
• Case 1: this happens for n = 0, giving x = 3/2 arctan(3).
• Case 2: this happens for n = 1, giving x = 9π/8.
• Case 3: this happens for n = 0, giving x = 3π/2 - 3/2 arctan(1/10).