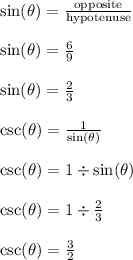Problem 3
Answer: 3/2
=====================================================
Step-by-step explanation:
Use the pythagorean theorem to find the length of the missing side.
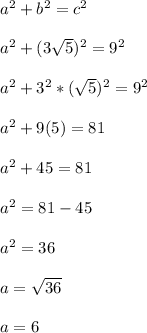
This is the length of the missing vertical side. This side is opposite the angle theta.
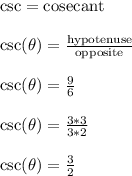
Alternatively, you can compute it like this