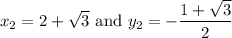Answer:
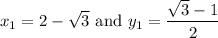
Or:
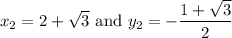
Explanation:
We are given the equation:
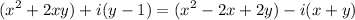
And we want to find the values of x and y such that the equation is true.
First, distribute:
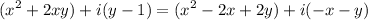
If two complex numbers are equivalent, their real and imaginary parts are equivalent. Hence:
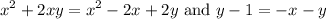
Simplify:
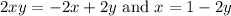
Substitute:
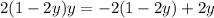
Solve for y:
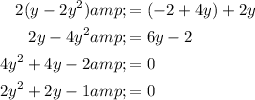
From the quadratic formula:
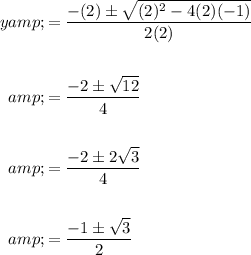
Hence:
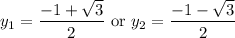
Then:
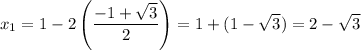
And:
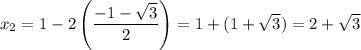
In conclusion, the values of x and y are:
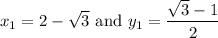
Or: