Differentiate both sides with respect to x and solve for the derivative dy/dx :
![(\mathrm d)/(\mathrm dx)\left[x^2y^2+xy\right] = (\mathrm d)/(\mathrm dx)[2] \\\\ (\mathrm d)/(\mathrm dx)\left[x^2\right]y^2 + x^2(\mathrm d)/(\mathrm dx)\left[y^2\right] + (\mathrm d)/(\mathrm dx)\left[x\right]y + x(\mathrm dy)/(\mathrm dx) = 0 \\\\ 2xy^2 + x^2(2y)(\mathrm dy)/(\mathrm dx) + y + x(\mathrm dy)/(\mathrm dx) = 0 \\\\ (2x^2y+x)(\mathrm dy)/(\mathrm dx) = -2xy^2-y \\\\ (\mathrm dy)/(\mathrm dx) = -(2xy^2+y)/(2x^2y+x)](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/mathematics/college/5pwrc6227hq3snxv3it1kvql5v1ceysz4z.png)
This gives the slope of the tangent to the curve at the point (x, y).
If the slope of some tangent line is -1, then
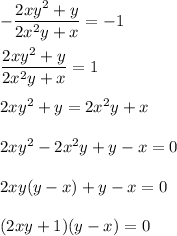
Then either
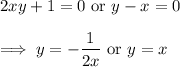
In the first case, we'd have
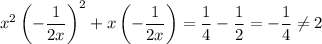
so this case is junk.
In the second case,
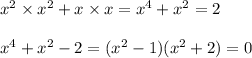
which means either
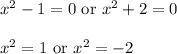
The second case here leads to non-real solutions, so we ignore it. The other case leads to
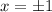 .
.
Find the y-coordinates of the points with x = ±1 :
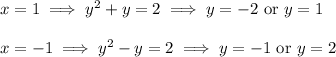
so the points of interest are (1, -2), (1, 1), (-1, -1), and (-1, 2).