Answer:
A
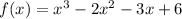
Explanation:
According to the Factor Theorem, if (x - k) is a factor of a polynomial P(x), then P(k) must equal zero.
We are given that a polynomial function has the zeros 2, √3, and -√3. So, we can let k = 2, √3, -√3.
So, according to the Factor Theorem, P(2), P(√3) and P(-√3) must equal 0.
Testing each choice, we can see that only A is true:
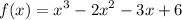
Testing all three values yields that:
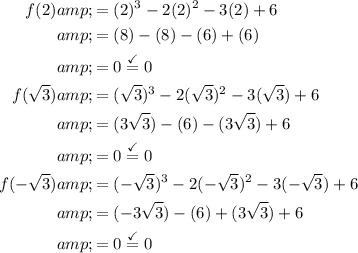
Hence, our answer is A.