Answer:
Choice A.
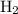 would be produced at the negative electrode.
would be produced at the negative electrode.
Step-by-step explanation:
Ionic equation for this reaction:
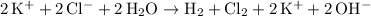 .
.
Net ionic equation:
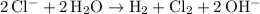 .
.
Half-equations:
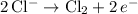 .
.
(Electrons travel from the solution to an electrode.)
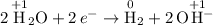 .
.
(An electrode supply electrons to the solution to reduce some of the
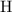 atoms from
atoms from
 .)
.)
In a DC circuit, electrons always enter the circuit from the negative terminal of the power supply and return to the power supply at the positive terminal.
The negative electrode is connected to the negative terminal of the power supply. Electrons from the power supply would flow into the solution through this electrode.
This continuous supply of electrons at the negative electrode would drive a reduction half-reaction. In this question, that corresponds to the reduction of water:
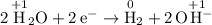 . Hence,
. Hence,
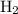 would be produced at the negative electrode.
would be produced at the negative electrode.