Answer:
Explanation:
If you drew out the bell curve and put the values where they go, this would be a no-brainer that doesn't even need math to solve. However, we will use the formula and then the table for z-scores to find this answer.
We are looking for the probability that the number of calls falls between 19 and 67. The standard deviation is 8 and the mean is 43. The probability we are looking for is P(19 < x < 67), therefore we look for the probability first that number of calls is greater than 19:
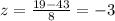 and from the table and to the right of the z-score, the probability that the number of calls is greater than 19 is .99865 (or 99.8%). Likewise,
and from the table and to the right of the z-score, the probability that the number of calls is greater than 19 is .99865 (or 99.8%). Likewise,
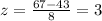 and from the table and to the right of the z-score, the probability that the number of calls is greater than 67 is .00315.
and from the table and to the right of the z-score, the probability that the number of calls is greater than 67 is .00315.
Take the difference of these to get the probability that the number of calls falls between these 2:
.99865 - .00135 = .9973 or 99.7%