Answer:
The magnitude of the magnetic field is 1.83 x
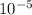 T.
T.
Step-by-step explanation:
The flow of an electric current in a straight wire induces magnetic field around the wire. When current is flowing through two wires in the same direction, a force of attraction exists between the wires. But if the current flows in opposite directions, the force of repulsion is felt by the wires.
In the given question, the direction of flow of current through the wires is opposite, thus both wires applies the same field on each other. The result to repulsion between them.
The magnetic field (B) between the given wires can be determined by:
B =
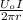
where: I is the current, r is the distance between the wires and
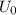 is the magnetic field constant.
is the magnetic field constant.
But, I = 11 A, r = 0.12 m and
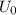 = 4
= 4
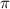 x
x
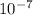 Tm/A
Tm/A
So that;
B =
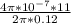
= 1.8333 x
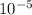
B = 1.83 x
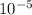 T
T