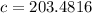Answer:
The expected total amount of time in minutes the operator will spend on the calls each day is of 174.8 minutes.
The standard deviation of the total amount of time in minutes the operator will spend on the calls each day is of 17.4356 minutes.
0.3085 = 30.85% approximate probability that the total time spent on the calls will be less than 166 minutes.
The value c such that the approximate probability that the total time spent on the calls each day is less than c is 0.95 is
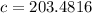
Explanation:
Normal Probability Distribution
Problems of normal distributions can be solved using the z-score formula.
In a set with mean
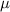 and standard deviation
and standard deviation
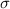 , the z-score of a measure X is given by:
, the z-score of a measure X is given by:
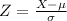
The Z-score measures how many standard deviations the measure is from the mean. After finding the Z-score, we look at the z-score table and find the p-value associated with this z-score. This p-value is the probability that the value of the measure is smaller than X, that is, the percentile of X. Subtracting 1 by the p-value, we get the probability that the value of the measure is greater than X.
n instances of a normally distributed variable:
For n instances of a normally distributed variable, the mean is:
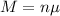
The standard deviation is:
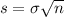
Calls to a customer service center last on average 2.3 minutes with a standard deviation of 2 minutes.
This means that
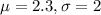
An operator in the call center is required to answer 76 calls each day.
This means that
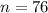
What is the expected total amount of time in minutes the operator will spend on the calls each day?
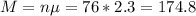
The expected total amount of time in minutes the operator will spend on the calls each day is of 174.8 minutes.
What is the standard deviation of the total amount of time in minutes the operator will spend on the calls each day?
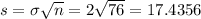
The standard deviation of the total amount of time in minutes the operator will spend on the calls each day is of 17.4356 minutes.
What is the approximate probability that the total time spent on the calls will be less than 166 minutes?
This is the p-value of Z when X = 166.
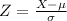
For this problem:
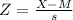
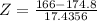
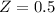
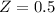 has a p-value of 0.6915.
has a p-value of 0.6915.
1 - 0.6915 = 0.3085.
0.3085 = 30.85% approximate probability that the total time spent on the calls will be less than 166 minutes.
What is the value c such that the approximate probability that the total time spent on the calls each day is less than c is 0.95?
This is X = c for which Z has a p-value of 0.95, so X = c when Z = 1.645. Then
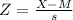
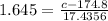
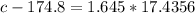
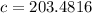
The value c such that the approximate probability that the total time spent on the calls each day is less than c is 0.95 is