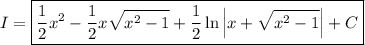I'm assuming the integral is
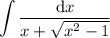
Rationalize the denominator:
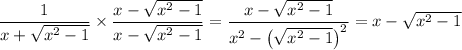
Then the integral is
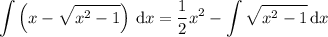
For the remaining integral, substitute x = sec(t ) and dx = sec(t ) tan(t ) dt. Then over an appropriate domain, we have
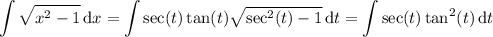
Integrate by parts, taking
u = tan(t ) ==> du = sec²(t ) dt
dv = sec(t ) tan(t ) dt ==> v = sec(t )
Then
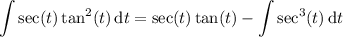
Now for *this* remaining integral, integrate by parts again, taking
u = sec(t ) ==> du = sec(t ) tan(t ) dt
dv = sec²(t ) dt ==> v = tan(t )
so that
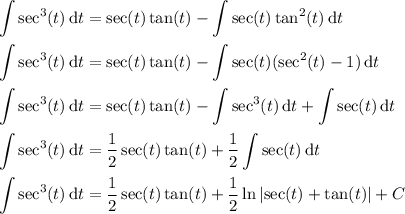
To summarize, if I denotes the original integral, we have
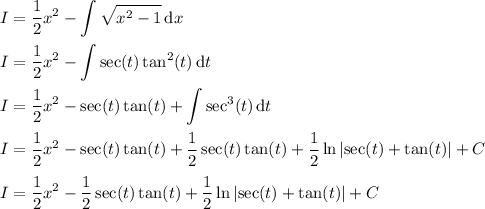
Putting everything back in terms of x, we have
sec(t ) = x
tan(t ) = √(x ² - 1)
so that