Answer:
The mechanical energy of the cardboard box, M.E. = K.E. + P.E.
Where;
P.E. = The potential energy of the cardboard box = m·g·h
K.E. = The kinetic energy of the cardboard box = (1/2)·m·v²
Where;
m = Mass of the cardboard box
g = The (constant) acceleration due to gravity ≈ 9.81 m/s²
h = The height of the cardboard box
v = The velocity of the cardboard box
At the top of the fall, where h = The height of the platform =
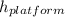 , and v = 0 (the box is initially at rest at the top), the M.E. is given as follows;
, and v = 0 (the box is initially at rest at the top), the M.E. is given as follows;
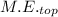 = P.E. + K.E. = m·g·
= P.E. + K.E. = m·g·
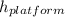 + (1/2) × m × 0² = m·g·
+ (1/2) × m × 0² = m·g·
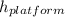
However, at the bottom of the fall, the height of the box, h = 0, the velocity of the box, v = 0, therefore, the total energy at the bottom, after the box comes to rest,
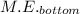 = 0
= 0
Therefore;
The total energy of the box at the top of the fall, .
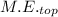 = m·g·
= m·g·
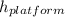 was more than the total energy of the box at the bottom of the fall,
was more than the total energy of the box at the bottom of the fall,
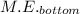 = 0
= 0
Step-by-step explanation: