The question is incomplete. The complete question is :
An analytical chemist is titrating 148.9 mL of a 1.100 M solution of benzoic acid
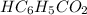 with a 0.3600 M solution of KOH. The
with a 0.3600 M solution of KOH. The
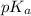 of benzoic acid is 4.20. Calculate the pH of the acid solution after the chemist has added 232.0 mL of the KOH solution to it. Note for advanced students: you may assume the final volume equals the initial volume of the solution plus the volume of KOH solution added.
of benzoic acid is 4.20. Calculate the pH of the acid solution after the chemist has added 232.0 mL of the KOH solution to it. Note for advanced students: you may assume the final volume equals the initial volume of the solution plus the volume of KOH solution added.
Solution :
Number of moles of
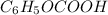
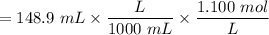
= 0.16379 mol
Number of moles of NaOH added
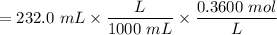
= 0.08352 mol
ICE table :
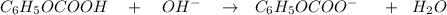
I (mol) 0.16379 0.08352 0
C (mol) -0.08352 -0.08352 +0.08352
E (mol) 0.08027 0 0.08352
Total volume = (148.9 + 232) mL
= 380.9 mL
= 0.3809 L
Concentration of
![$C_6H_5OCOOH, [C_6H_5OCOOH]$](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/chemistry/college/k6xqtawnuta7qz9gbg086tud8ak81yrn97.png)
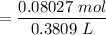
= 0.211 M
Concentration of
![$C_6H_5OCOO^- , [C_6H_5OCOO^-] =(0.08352 \ mol)/(0.3809 \ L)](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/chemistry/college/o4sk1wclj4vim14x0hfs35jkgiklzg2i1z.png)
= 0.219 M
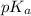 of
of
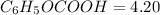
According to Henderson equation,
![$pH = pK_a + \log ([C_6H_5OCOO^-])/([C_6H_5OCOOH])](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/chemistry/college/nxsgt64bu9hbk3xlfdnf0w8xfsjbtqga5x.png)
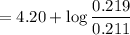
= 4.22
Therefore, the pH of the acid solution is 4.22