Solution :
Molecular Molar Mass Volume Density Mass Moles nmoles
formula (g/mol) (mL) (g/mL) (g)
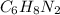 108.14 0.108 0.001 1
108.14 0.108 0.001 1
HCOOH 46.02 0.064 1.22 0.07808 0.0017 1.7
mmoles of o-phenylenediamine = 1 mmoles
mmoles of formic acid = 1.7
 2 mmoles
2 mmoles
From the reaction of o-phenylenediamine and formic acid, we see,
1 mmole of o-phenylenediamine reacts with 1 mmole of formic acid.
But here, 2 mmoles of the formic acid , this means that the formic acid is an excess reagent and the o-phenylenediamine is the limiting reagent here.
The amount of product depends on the limiting reagent that is o-phenylenediamine. So, 1mmole of o-phenylenediamine will give 1mmole of product.
molar mass of Benzimidazole =
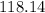 g/mol
g/mol
mmoles of Benzimidazole formed =
 mmol
mmol
Mass of benzimidazole formed = molar mass x
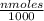
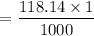
= 0.11814 g
So the theoretical yield of Benzimidazole is = 0.118 g = 118mg