Answer:
Number of moles, n = 68.20 moles
Step-by-step explanation:
Given the following data;
- Volume, V = 2200 m³
- Temperature, T = 388 K
- Pressure, P = 100 kPa
- Ideal gas constant, R = 8.314 J/mol·K or 0.08206 L·atm·mol−1·K−1
To find the number of moles, we would use the ideal gas law equation;
PV = nRT
Where;
- P is the pressure.
- V is the volume.
- n is the number of moles of substance.
- R is the ideal gas constant.
- T is the temperature.
Making n the subject of formula, we have;
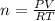
Substituting into the formula, we have;
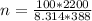
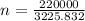
Number of moles, n = 68.20 moles