Answer:
A. A critical value is how far away our sample statistic can be from the true population parameter with a certain level of confidence.
Explanation:
Test of a hypothesis:
When we are testing a hypothesis, we have a null hypothesis and an alternative hypothesis, and the conclusion depends on the test statistic, given by:
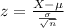
In which X is the sample mean,
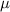 is the value tested at the null hypothesis,
is the value tested at the null hypothesis,
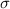 is the standard deviation and n is the size of the sample.
is the standard deviation and n is the size of the sample.
The test statistic measures the number of standard errors that we have to move away from the sample mean, and the critical value is how much we can be far from the population parameter with a certain level of confidence, that is, before a certain value we do not reject the null hypothesis, after the value we reject, and this value is the critical value, and thus the correct answer is given by option a.