Answer:
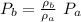
Step-by-step explanation:
The pressure at a depth of a fluid is
P = ρ g y
where ρ is the density of the fluid, y the depth of the gauge measured from the surface of the fluid.
In this case the pressure for fluid A is
Pa = ρₐ g y
the pressure for fluid B is
P_b = ρ_b g y
depth y not changes as the gauge is stationary
if we look for the relationship between these pressures
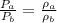
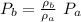
therefore we see that the pressure measured for fluid B is different from the pressure of fluid A
if ρₐ < ρ_b B the pressure P_b is greater than the initial reading
ρₐ> ρ_b the pressure in B decreases with respect to the reading in liquid A