Answer:
The p-value of the test is 0.2262 > 0.02, which means that the decision is to fail to reject the null hypothesis.
Explanation:
An automobile manufacturer has given its jeep a 51.3 miles/gallon (MPG) rating.
At the null hypothesis, we test if the mean is of 51.3, that is:
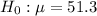
An independent testing firm has been contracted to test the actual MPG for this jeep since it is believed that the jeep has an incorrect manufacturer's MPG rating.
This means that at the alternative hypothesis, we test if the mean is different of 51.3, that is:
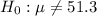
The test statistic is:
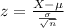
In which X is the sample mean,
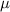 is the value tested at the null hypothesis,
is the value tested at the null hypothesis,
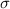 is the standard deviation and n is the size of the sample.
is the standard deviation and n is the size of the sample.
51.3 is tested at the null hypothesis:
This means that
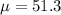
After testing 230 jeeps, they found a mean MPG of 51.1. Assume the population variance is known to be 6.25.
This means that
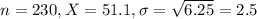
Value of the test statistic:
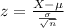
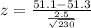
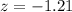
P-value of the test and decision:
The p-value of the test is the probability of the sample mean differing from 51.1 by at least 0.2, which is P(|z| > 1.21), which is 2 multiplied by the p-value of z = -1.21.
Looking at the z-table, z = -1.21 has a p-value of 0.1131.
2*0.1131 = 0.2262
The p-value of the test is 0.2262 > 0.02, which means that the decision is to fail to reject the null hypothesis.