Answer:
The p-value of the test statistic is 0.2019.
Explanation:
Test if there is evidence at the 0.02 level that the medicine relieves pain in more than 384 seconds.
At the null hypothesis, we test if it relieves pain in at most 384 seconds, that is:
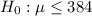
At the alternative hypothesis, we test if it relieves pain in more than 384 seconds, that is:
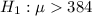
The test statistic is:
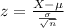
In which X is the sample mean,
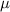 is the value tested at the null hypothesis,
is the value tested at the null hypothesis,
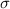 is the standard deviation and n is the size of the sample.
is the standard deviation and n is the size of the sample.
384 is tested at the null hypothesis:
This means that
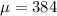
For a sample of 41 patients, the mean time in which the medicine relieved pain was 387 seconds. Assume the population standard deviation is 23.
This means that
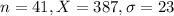
Value of the test statistic:
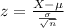
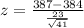
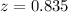
P-value of the test:
The p-value of the test is the probability of finding a sample mean above 387, which is 1 subtracted by the p-value of z = 0.835.
Looking at the z-table, z = 0.835 has a p-value of 0.7981.
1 - 0.7981 = 0.2019
The p-value of the test statistic is 0.2019.