Answer:
So, remember that:
cos(x) > 0 for -pi/2 < x < pi/2
cos(x) < 0 for pi/2 < x < (3/2)*pi
and
sin(x) > 0 for 0 < x < pi
sin(x) < 0 for -pi < x <0 or pi < x < 2pi
Also, we have the periodicty of the sine and cocine equations, such that:
sin(x) = sin(x + 2pi)
cos(x) = cos(x + 2pi)
Now let's solve the problem:
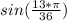
here we have:
x = (13/36)π
This is larger than zero and smaller than π:
0 < (13/36)π < π
then:
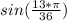
Is positive.
The next one is:
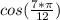
Here we have x = (7/12)*pi
notice that:
7/12 > 1/2
Then:
(7/12)*π > (1/2)*π
Then:
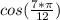
is negative.
next one:
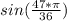
here:
x = (47/36)*π
here we have (47/36) > 1
then:
(47/36)*π > π
then:
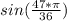
is negative.
the next one is:
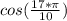
Here we have x = (17/10)*π
if we subtract 2*π (because of the periodicity) we get:
(17/10)*π - 2*π
(17/10)*π - (20/10)*π
(-3/10)*π
this is in the range where the cosine function is positive, thus:
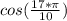
is positive.
the next one is:
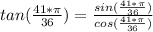
here we have:
x = (41/36)*π
Notice that both functions, sine and cosine are negatives for that value, then we have the quotient of two negative values, so:
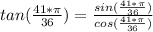
is positive.
The final one is:
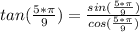
Here:
x = (5/9)*π
The sin function is positive with this x value, while the cosine function is negative, thus:
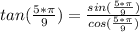
Is negative.