Answer:
The 99% confidence interval estimate of the percentage of girls born is (86.04%, 93.96%). Considering the actual percentage of girls born is close to 50%, the percentage increased considerably with this method, which means that it appears effective.
Explanation:
In a sample with a number n of people surveyed with a probability of a success of
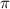 , and a confidence level of
, and a confidence level of
 , we have the following confidence interval of proportions.
, we have the following confidence interval of proportions.
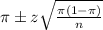
In which
z is the z-score that has a p-value of
 .
.
In the study 380 babies were born, and 342 of them were girls.
This means that
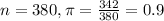
99% confidence level
So
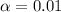 , z is the value of Z that has a p-value of
, z is the value of Z that has a p-value of
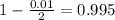 , so
, so
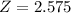 .
.
The lower limit of this interval is:
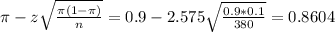
The upper limit of this interval is:
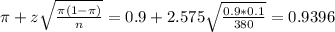
As percentages:
0.8604*100% = 86.04%.
0.9396*100% = 93.96%.
The 99% confidence interval estimate of the percentage of girls born is (86.04%, 93.96%). Considering the actual percentage of girls born is close to 50%, the percentage increased considerably with this method, which means that it appears effective.