Answer:
Since
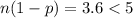 , the normal distribution cannot be used as an approximation to the binomial probability to approximate the probability.
, the normal distribution cannot be used as an approximation to the binomial probability to approximate the probability.
Using the binomial distribution, 100% probability that more than 97 out of 120 people will get the flu this winter.
Explanation:
Binomial probability distribution
The binomial probability is the probability of exactly x successes on n repeated trials, and X can only have two outcomes.
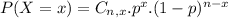
In which
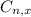 is the number of different combinations of x objects from a set of n elements, given by the following formula.
is the number of different combinations of x objects from a set of n elements, given by the following formula.
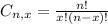
And p is the probability of X happening.
Can be approximated to a normal distribution, using the expected value and the standard deviation.
The expected value of the binomial distribution is:
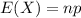
The standard deviation of the binomial distribution is:
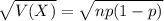
Normal probability distribution
Problems of normally distributed distributions can be solved using the z-score formula.
In a set with mean
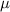 and standard deviation
and standard deviation
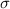 , the zscore of a measure X is given by:
, the zscore of a measure X is given by:
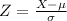
The Z-score measures how many standard deviations the measure is from the mean. After finding the Z-score, we look at the z-score table and find the p-value associated with this z-score. This p-value is the probability that the value of the measure is smaller than X, that is, the percentile of X. Subtracting 1 by the pvalue, we get the probability that the value of the measure is greater than X.
When we are approximating a binomial distribution to a normal one, we have that
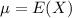 ,
,
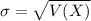 .
.
Assume the probability that a given person will get the flu this winter is 97%.
This means that
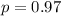
120 people
This means that
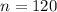
Verifying the necessary conditions.
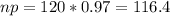
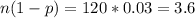
Since
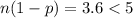 , the normal distribution cannot be used as an approximation to the binomial probability to approximate the probability. Thus, the binomial distribution has to be used.
, the normal distribution cannot be used as an approximation to the binomial probability to approximate the probability. Thus, the binomial distribution has to be used.
Probability using the binomial distribution:
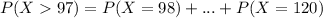
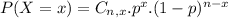
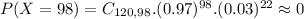
Probability close to 0, but below the mean, which means that the probability of the number being above this is 100%.
Using the binomial distribution, 100% probability that more than 97 out of 120 people will get the flu this winter.