Answer:
a) v = 0.18 m / s, b) K₀ₐ = 0.0378 J, c) K_{ob}= 0, d) K = 0.02349 J,
Step-by-step explanation:
a) For this exercise we must define a system formed by the two cars, so that the forces during the collision are internal and the moment is conserved
initial instant. Before the hole
p₀ = ma v₀ₐ
final intnate. After the crash
p_f = (mₐ + m_b) v
the moment is preserved
p₀ = p_f
mₐ v₀ₐ = (mₐ + m_b) v
v =
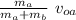
let's calculate
v =
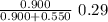
v = 0.18 m / s
in the same direction of the movement of carriage A
b) the initial kinetic energy car A
K₀ₐ = ½ m v₀ₐ²
K₀ₐ = ½ 0.900 0.29²
K₀ₐ = 0.0378 J
c) kinetic energy of carriage B
k_{ob} = 0
because the car is stopped
d) the kinetic energy of the system
K = ½ (mₐ + m_b) v²
K = ½ (0.900 + 0.550) 0.18²
K = 0.02349 J
E) we see that part of the kinetic energy is lost, therefore the scientific reeling is not conserved in inelastic collisions
F) and momentum is conserved since it is equal to the variation of the moment and this is conserved in all collisions