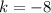Answer:
Explanation:
According to the Polynomial Remainder Theorem, if we have a polynomial P(x) divided by a binomial in the form of (x - a), then the remainder will be given by P(a).
And according to the Factor Theorem, if the remainder of P(x) / (x - a) is zero: that is, if P(a) = 0, then (x - a) is a factor of P(x).
We are given the polynomial:
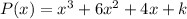
And we know that it is divisible by:
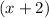
We can rewrite our divisor as (x - (-2)). Hence, a = -2.
According to both the PRT and Factor Theorem, P(-2) must equal 0. Hence:
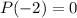
Substitute:
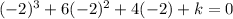
Solve for k. Simplify:
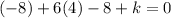
Hence: