Answer:
the entropy change for the system when 1.58 moles of CaCO3(s) react at standard conditions is 253.748 J/K
Step-by-step explanation:
Given the data in the question;
CaCO₃(s) → CaO(s) + CO₂(g)
1.58 moles 1.58 moles 1.58 moles
Since 1 mole of CaCO₃ gives 1 mole of CaO and 1 mole of CO₂
Thus, 1.58 mole of CaCO₃ gives 1.58 moles of CaO and 1.58 moles of CO₂.
Now,
At 298 K, standard entropy values are;
ΔS° ( CaCO₃ ) = 92.9 J/mol.K
ΔS° ( CaO ) = 39.8 J/mol.K
ΔS° ( CO₂ ) = 213.7 J/mol.K
So,
ΔS°
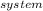 = ∑ΔS°( product ) - ∑ΔS°( reactant )
= ∑ΔS°( product ) - ∑ΔS°( reactant )
ΔS°
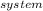 = [ ΔS°(CaO) + ΔS°( CO₂ ) ] - ΔS°( CaCO₃ )
= [ ΔS°(CaO) + ΔS°( CO₂ ) ] - ΔS°( CaCO₃ )
we substitute
ΔS°
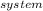 = [ 39.8 J/mol.K + 213.7 J/mol.K ] - 92.9 J/mol.K
= [ 39.8 J/mol.K + 213.7 J/mol.K ] - 92.9 J/mol.K
ΔS°
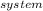 = 160.6 J/mol.K
= 160.6 J/mol.K
i.e, for 1 mol CaCO₃, ΔS°
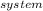 = 160.6 J/mol.K
= 160.6 J/mol.K
Now, for 1.58 mol CaCO₃,
ΔS°
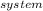 = 1.58 mol × 160.6 J/mol.K
= 1.58 mol × 160.6 J/mol.K
ΔS°
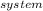 = 253.748 J/K
= 253.748 J/K
Therefore, the entropy change for the system when 1.58 moles of CaCO3(s) react at standard conditions is 253.748 J/K