Answer:
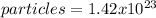
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello there!
In this case, according to the given information, it turns out possible for us solve this problem by using the ideal gas law:
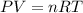
Which can be modified to include the particles in terms of the Avogadro's number:
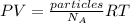
Thus, if we solve for the particles, we will obtain the expression and the numerical result:
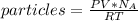
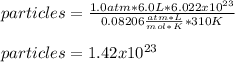
Regards!