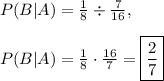Answer:
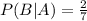
Step-by-step explanation:
The probability of
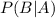 can be read as the probability of event B occurring given event A. In this question, event A occurs when the chosen player is a girl. There are 7 girls on the soccer team. Event B occurs when the chose player plays defense. Since
can be read as the probability of event B occurring given event A. In this question, event A occurs when the chosen player is a girl. There are 7 girls on the soccer team. Event B occurs when the chose player plays defense. Since
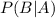 stipulates that event A already occurred, we want the probability of choosing a player who prefers defense from the 7 girls. There are 2 girls who prefer defense, hence
stipulates that event A already occurred, we want the probability of choosing a player who prefers defense from the 7 girls. There are 2 girls who prefer defense, hence
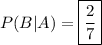 .
.
Alternative:
For dependent events
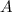 and
and
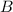 , the conditional probability of event B occurring given A is given by:
, the conditional probability of event B occurring given A is given by:
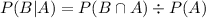
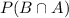 indicates the intersection of
indicates the intersection of
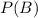 and
and
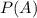 . In this case, it is the probability that both events occur. Since there are 16 kids on the soccer team and only 2 are girls and prefer defense,
. In this case, it is the probability that both events occur. Since there are 16 kids on the soccer team and only 2 are girls and prefer defense,
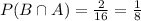 . The probability of event A occurring (chosen player is a girl) is equal to the number of girls (7) divided by the number of kids on the team (16), hence
. The probability of event A occurring (chosen player is a girl) is equal to the number of girls (7) divided by the number of kids on the team (16), hence
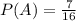 .
.
Therefore, the probability of event B occurring, given event A occurred, is equal to: