Given:
The recursive formulae.
To find:
The correct explicit formulae for the given recursive formulae.
Solution:
If the recursive formula of a GP is
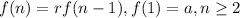 , then the explicit formula of that GP is:
, then the explicit formula of that GP is:
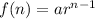
Where, a is the first term and r is the common ratio.
The first recursive formula is:
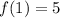
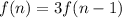 for
for
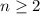 .
.
It is the recursive formula of a GP with a=5 and r=3. So, the required explicit formula is:
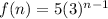
Therefore, the required explicit formula for the first recursive formula is
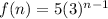 .
.
If the recursive formula of an AP is
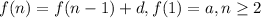 , then the explicit formula of that AP is:
, then the explicit formula of that AP is:
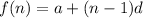
Where, a is the first term and d is the common difference.
The second recursive formula is:
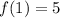
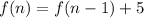 for
for
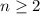 .
.
It is the recursive formula of an AP with a=5 and d=5. So, the required explicit formula is:
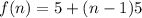
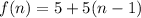
Therefore, the required explicit formula for the second recursive formula is
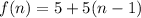 .
.
The third recursive formula is:
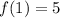
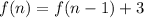 for
for
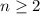 .
.
It is the recursive formula of an AP with a=5 and d=3. So, the required explicit formula is:
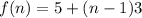
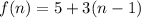
Therefore, the required explicit formula for the third recursive formula is
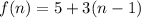 .
.