Answer:
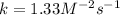
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello there!
In this case, according to the given information for the definition of the rate law, which is second-order with respect to NO2 and first-order to O2, we can solve for k as both concentrations are given as well as the initial rate of reaction:
![k=(r)/([NO_2]^2[O_2])](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/chemistry/college/hyzy5aorl0ev8rbgujozjukvfvpj95z498.png)
In such a way, we can just plug in the given values to obtain the correct rate constant with the appropriate units:
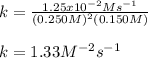
Regards!