Answer:
1,900 J
Step-by-step explanation:
The number of moles of helium gas, n = 2 moles
The pressure of the helium gas, p = 1.0 × 10⁵ Pa
The initial temperature of the gas, T₁ = 2°C = 275.15 K
The final temperature of the gas, T₂ = 112°C = 385.15 K
The initial volume of the gas, V₁ = 45 liters
Cp = 20.8 J/(mol·K), Cv = 12.6 J/(mol·K)
The work done by the gas having constant pressure expansion is given as follows;
From the ideal gas law, we have;
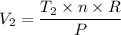
Where;
R = The universal gas constant = 8.314 J/(mol×K)
Therefore, we get;
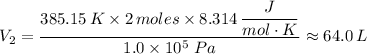
The work done, W = P ×ΔV = P × (V₂ - V₁)
∴ W = 1.0 × 10⁵ Pa × (64.0 L - 45.0 L) = 1,900 J
The work done by the gas as it expands, W = 1,900 J.