Answer:
10.71%
Step-by-step explanation:
The dissociation of acetic acid can be well expressed as follow:
CH₃COOH ⇄ CH₃COO⁻ + H⁺
Let assume that the prepared amount of the aqueous solution is 14mM since it is not given:
Then:
The I.C.E Table is expressed as follows:
CH₃COOH ⇄ CH₃COO⁻ + H⁺
Initial 0.0014 0 0
Change - x +x +x
Equilibrium (0.0014 - x) x x
Recall that:
Ka for acetic acid CH₃COOH = 1.8×10⁻⁵
∴
![K_a = ([x][x]])/([0.0014-x])](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/chemistry/college/imspiyeyr6f28jrdvxnqd8nz5hq9xr5wbt.png)
![1.8*10^(-5) = ([x][x]])/([0.0014-x])](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/chemistry/college/y7eqlptearuuv34gb19x76j5mzalpcjyga.png)
![1.8*10^(-5) = ([x]^2)/([0.0014-x])](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/chemistry/college/e8cw15ik1lyp12gy9ch5tm9ptjzqc94ud4.png)
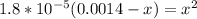
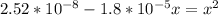
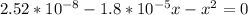
By rearrangement:
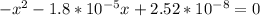
Multiplying through by (-) and solving the quadratic equation:
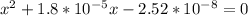
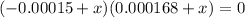
x = 0.00015 or x = -0.000168
We will only consider the positive value;
so x=[CH₃COO⁻] = [H⁺] = 0.00015
CH₃COOH = (0.0014 - 0.00015) = 0.00125
However, the percentage fraction of the dissociated acetic acid is:
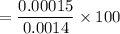
= 10.71%