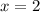Answer:
The domain of the function is all real values of x, except
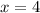 and
and
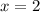
Explanation:
We are given the following function:
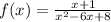
It's a fraction, so the domain is all the real values except those in which the denominator is 0.
Denominator:
Quadratic equation with
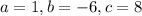
Using bhaskara, the denominator is 0 for these following values of x:
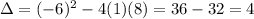
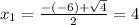
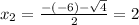
The domain of the function is all real values of x, except
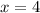 and
and