Answer:
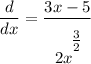
General Formulas and Concepts:
Algebra I
- Exponential Rule [Powering]:
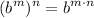
- Exponential Rule [Rewrite]:
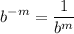
- Exponential Rule [Root Rewrite]:
![\displaystyle \sqrt[n]{x} = x^{(1)/(n)}](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/mathematics/college/yqpyvbuov0tgbjo8vla0qsqp67pafn2fr7.png)
Calculus
Derivatives
Derivative Notation
Derivative Property [Addition/Subtraction]:
![\displaystyle (d)/(dx)[f(x) + g(x)] = (d)/(dx)[f(x)] + (d)/(dx)[g(x)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/mathematics/high-school/i90hl6t3gcguvrecodn8t9gnodav0w5ns8.png)
Basic Power Rule:
- f(x) = cxⁿ
- f’(x) = c·nxⁿ⁻¹
Derivative Rule [Quotient Rule]:
![\displaystyle (d)/(dx) [(f(x))/(g(x)) ]=(g(x)f'(x)-g'(x)f(x))/(g^2(x))](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/mathematics/high-school/hrfl3gpx3dh352g7a9uj6guyxz9uxwhvl3.png)
Explanation:
Step 1: Define
Identify
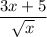
Step 2: Differentiate
- Rewrite [Exponential Rule - Root Rewrite]:
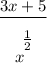
- Quotient Rule:
![\displaystyle (d)/(dx) = \frac{(x^\bigg{(1)/(2)})(d)/(dx)[3x + 5] - (d)/(dx)[x^\bigg{(1)/(2)}](3x + 5)}{(x^\bigg{(1)/(2)})^2}](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/mathematics/college/pyj7kbfilnkcnt6wgajxg7nd012qegmpz1.png)
- Simplify [Exponential Rule - Powering]:
![\displaystyle (d)/(dx) = \frac{(x^\bigg{(1)/(2)})(d)/(dx)[3x + 5] - (d)/(dx)[x^\bigg{(1)/(2)}](3x + 5)}{x}](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/mathematics/college/w4gs1byd4lrihsnh8of5dyvnk3m2f24wxs.png)
- Basic Power Rule [Derivative Property - Addition/Subtraction]:
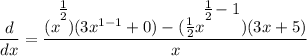
- Simplify:
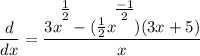
- Rewrite [Exponential Rule - Rewrite]:
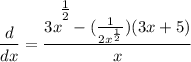
- Rewrite [Exponential Rule - Root Rewrite]:
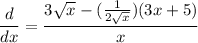
- Simplify [Rationalize]:
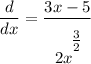
Topic: AP Calculus AB/BC (Calculus I/I + II)
Unit: Derivatives
Book: College Calculus 10e