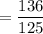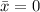
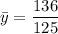
Explanation:
Let's define our functions
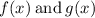 as follows:
as follows:
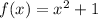
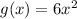
The two functions intersect when
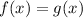 and that occurs at
and that occurs at
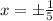 so they're going to be the limits of integration. To solve for the coordinates of the centroid
so they're going to be the limits of integration. To solve for the coordinates of the centroid
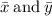 , we need to solve for the area A first:
, we need to solve for the area A first:
![\displaystyle A = \int_a^b [f(x) - g(x)]dx](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/mathematics/college/1ydwazsoxy358z3huwr3cjfgtfgtn169us.png)
![\displaystyle \:\:\:\:\:\:\:=\int_{-(1)/(5)}^{+(1)/(5)}[(x^2 + 1) - 6x^2]dx](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/mathematics/college/mqsycrma12wictvm0fdcmnra9q4yqk14ff.png)
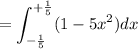
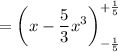
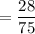
The x-coordinate of the centroid
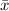 is given by
is given by
![\displaystyle \bar{x} = (1)/(A)\int_a^b x[f(x) - g(x)]dx](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/mathematics/college/a03ga5u0bn734j34u2ab5or0stmfit6iyq.png)
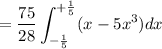
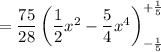
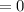
The y-coordinate of the centroid
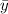 is given by
is given by
![\displaystyle \bar{y} = (1)/(A)\int_a^b (1)/(2)[f^2(x) - g^2(x)]dx](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/mathematics/college/5y63co0vswi4pfdwawqu0uiehq96387vj8.png)
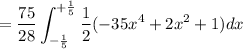
![\:\:\:\:\:\:\:=(75)/(56) \left[-7x^5 + (2)/(3)x^3 + x \right]_{-(1)/(5)}^{+(1)/(5)}](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/mathematics/college/nho15qs7o82ssdin8xibinkyjk59r9ws2k.png)