Answer:
25.08 grams of O₂ are needed to react with 8.15 g of C₂H₂.
Step-by-step explanation:
The balanced reaction is:
2 C₂H₂ + 5 O₂ → 4 CO₂ + 2 H₂O
By reaction stoichiometry, the following amounts of moles of each compound participate in the reaction:
- C₂H₂: 2 moles
- O₂: 5 moles
- CO₂: 4 moles
- H₂O: 2 moles
The molar mass of each compound is:
- C₂H₂: 26 g/mole
- O₂: 32 g/mole
- CO₂: 44 g/mole
- H₂O: 18 g/mole
Then, by reaction stoichiometry, the following mass quantities of each compound participate in the reaction:
- C₂H₂: 2 moles* 26 g/mole= 52 g
- O₂: 5 moles* 32 g/mole= 160 g
- CO₂: 4 moles* 44 g/mole= 176 g
- H₂O: 2 moles* 18 g/mole= 36 g
Then you can apply the following rule of three: if by stoichiometry 52 grams of C₂H₂ react with 160 grams of O₂, 8.15 grams of C₂H₂ react with how much mass of O₂?
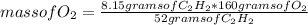
mass of O₂= 25.08 grams
25.08 grams of O₂ are needed to react with 8.15 g of C₂H₂.