Answer:
0.7994 = 79.94% probability that the proportion of persons with myopia will differ from the population proportion by less than 3%.
Explanation:
To solve this question, we need to understand the normal probability distribution and the central limit theorem.
Normal Probability Distribution
Problems of normal distributions can be solved using the z-score formula.
In a set with mean
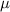 and standard deviation
and standard deviation
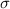 , the z-score of a measure X is given by:
, the z-score of a measure X is given by:
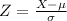
The Z-score measures how many standard deviations the measure is from the mean. After finding the Z-score, we look at the z-score table and find the p-value associated with this z-score. This p-value is the probability that the value of the measure is smaller than X, that is, the percentile of X. Subtracting 1 by the p-value, we get the probability that the value of the measure is greater than X.
Central Limit Theorem
The Central Limit Theorem establishes that, for a normally distributed random variable X, with mean
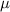 and standard deviation
and standard deviation
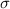 , the sampling distribution of the sample means with size n can be approximated to a normal distribution with mean
, the sampling distribution of the sample means with size n can be approximated to a normal distribution with mean
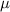 and standard deviation
and standard deviation
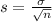 .
.
For a skewed variable, the Central Limit Theorem can also be applied, as long as n is at least 30.
For a proportion p in a sample of size n, the sampling distribution of the sample proportion will be approximately normal with mean
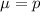 and standard deviation
and standard deviation
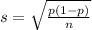
Suppose 42% of the population has myopia.
This means that
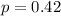
Random sample of size 442 is selected
This means that
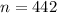
Mean and standard deviation:
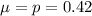
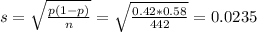
What is the probability that the proportion of persons with myopia will differ from the population proportion by less than 3%?
Proportion between 0.42 + 0.03 = 0.45 and 0.42 - 0.03 = 0.39, which is the p-value of Z when X = 0.45 subtracted by the p-value of Z when X = 0.39.
X = 0.45
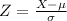
By the Central Limit Theorem
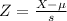
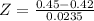
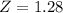
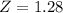 has a p-value of 0.8997
has a p-value of 0.8997
X = 0.39
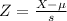
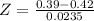

 has a p-value of 0.1003
has a p-value of 0.1003
0.8997 - 0.1003 = 0.7994
0.7994 = 79.94% probability that the proportion of persons with myopia will differ from the population proportion by less than 3%.