Answer:
v = 1.23 m / s
the stone goes in the initial direction of the ball.
Step-by-step explanation:
This is a momentum conservation problem, they indicate that after the crash its speed is 70% of its initial energy.
K_f = 0.7 K₀
½ m v_f² = 0.7 ½ m v₀²
v_f² = 0.7 v₀²
v_f = √0.7 v₀
v_f = √0.7 20
v_f = 16.73 m / s
now we can use conservation the moment
initial instant. Before the crash
p₀ = m v₀ + 0
final instant. After the crash
p_f = m v_f + M v
p₀ = p_f
m v₀ = m v_f + M v
v =
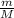 (v₀ - v_f)
(v₀ - v_f)
v = 0.750 (20 - 16.73) / M
v = 2.4525 / M
To finish the exercise we must assume a mass of the stone, generally higher than the mass of the ball.
M = 2 kg
v = 2.4525 / 2
v = 1.23 m / s
the stone goes in the initial direction of the ball.