Answer:
The p-value is 0.2789 > 0.05, which means that the appropriate conclusion is that the students do not score differently.
Explanation:
It is believed that students who begin studying for final exams a week before the test score differently than students who wait until the night before.
At the null hypothesis, we test if the two means are equal, that is, the subtraction of them is 0.
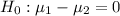
At the alternative hypothesis, we test if the two means are different, that is, the subtraction of them is different of 0. So
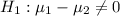
A hypothesis test for two independent samples is run based on your data and a p-value is calculated to be 0.2789.
Considering a standard significance level of 0.02789, the p-value is 0.2789 > 0.05, which means that the appropriate conclusion is that the students do not score differently.