This question is incomplete, the complete question is;
A sample of polystyrene, which has a specific heat capacity of 1.880 J.g⁻¹, is put into a calorimeter (see sketch at right) that contains 300.0 g of water. The polystyrene sample starts off at 94.9 °C and the temperature of the water starts off at 22.0. When the temperature of the water stops changing it's 27 °C . The pressure remains constant at 1 atm.
Calculate the mass of the polystyrene sample. Be sure your answer is rounded to 2 significant digits.
Answer:
the mass of the polystyrene sample is 57 g
Step-by-step explanation:
Given the data in the question;
mass of water m
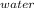 = 300 g
= 300 g
Temperature of water T
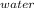 = 22 °C
= 22 °C
Specific heat capacity of water C
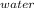 = 4.184 J/g°C
= 4.184 J/g°C
mass of the polystyrene sample m
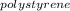 = ?
= ?
T
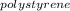 = 94.9 °C
= 94.9 °C
Specific heat capacity of polystyrene; C
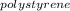 = 1.880 J.g⁻¹.°C⁻¹
= 1.880 J.g⁻¹.°C⁻¹
T = 27.7 °C
Now, using heat conservation equation
heat lost by polystyrene = heat gained by water
m
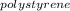 × C
× C
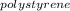 × ( T
× ( T
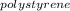 - T ) = m
- T ) = m
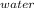 × C
× C
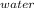 × ( T - T
× ( T - T
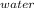 )
)
We substitute
m
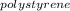 × 1.880 × ( 94.9 - 27.7 ) = 300 × 4.184 × ( 27.7 - 22 )
× 1.880 × ( 94.9 - 27.7 ) = 300 × 4.184 × ( 27.7 - 22 )
m
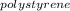 × 1.880 × 67.2 = 300 × 4.184 × 5.7
× 1.880 × 67.2 = 300 × 4.184 × 5.7
m
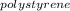 × 126.336 = 7154.64
× 126.336 = 7154.64
m
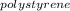 = 7154.64 / 126.336
= 7154.64 / 126.336
m
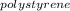 = 56.63 ≈ 57 g { 2 significant figures }
= 56.63 ≈ 57 g { 2 significant figures }
Therefore, the mass of the polystyrene sample is 57 g