Answer: The molecular weight of the dibasic acid is 89.6 g/mol
Step-by-step explanation:
Normality is defined as the amount of solute expressed in the number of gram equivalents present per liter of solution. The units of normality are eq/L. The formula used to calculate normality:
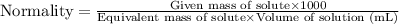 ....(1)
....(1)
We are given:
Normality of solution =
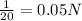
Given mass of solute = 0.56 g
Volume of solution = 250 mL
Putting values in equation 1, we get:
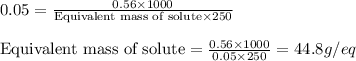
Equivalent weight of an acid is calculated by using the equation:
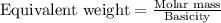 .....(2)
.....(2)
Equivalent weight of acid = 44.8 g/eq
Basicity of an acid = 2 eq/mol
Putting values in equation 2, we get:
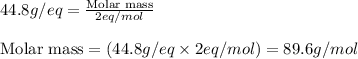
Hence, the molecular weight of the dibasic acid is 89.6 g/mol