Answer:
See explanation.
General Formulas and Concepts:
Pre-Algebra
Order of Operations: BPEMDAS
- Brackets
- Parenthesis
- Exponents
- Multiplication
- Division
- Addition
- Subtraction
Algebra I
- Functions
- Function Notation
Calculus
Limits
- Right-Side Limit:
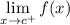
- Left-Side Limit:
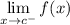
Limit Rule [Variable Direct Substitution]:
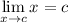
Explanation:
Step 1: Define
Identify
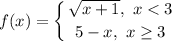
Step 2: Find Right Limit
- Substitute in variables [Right-Side Limit]:

- Evaluate limit [Limit Rule - Variable Direct Substitution]:
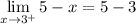
- Subtract:
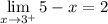
∴ the right-side limit equals 2.
Step 3: Find Left Limit
- Substitute in variables [Left-Side Limit]:

- Evaluate limit [Limit Rule - Variable Direct Substitution]:
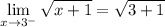
- [√Radical] Add:
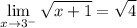
- [√Radical] Evaluate:

∴ the left-side limit equals 2.
Step 4: Find Limit
The right and left-side limits are equal.
∴

Topic: AP Calculus AB/BC (Calculus I/I + II)
Unit: Limits
Book: College Calculus 10e