Answer:
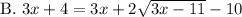 only for
only for
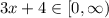
Explanation:
Key formulas used:
Given
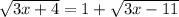 ,
,
We can use the first formula on the left side of the equation.
In this case, for
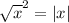 ,
,
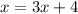 , we have:
, we have:
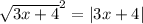
Similarly, we can use the second formula on the right side of the equation.
In this case, for
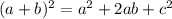 ,
,
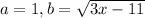 , we have:
, we have:
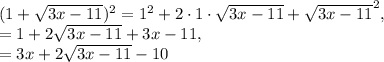
Therefore, when you square both sides of the equation, you get:
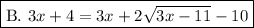
*Important:
This answer choice is actually only correct if
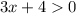 , because of the first formula we used. If
, because of the first formula we used. If
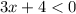 (negative), then
(negative), then
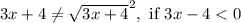 . Graphically, you can show this since the line
. Graphically, you can show this since the line
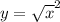 is not equal to
is not equal to
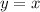 but instead
but instead
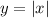 .
.
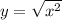 and
and
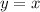 only overlap if you restrict the domain to
only overlap if you restrict the domain to
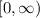 (positive numbers), hence
(positive numbers), hence
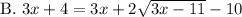 only for
only for
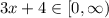 .
.