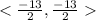Answer:
a. <-13/2,-13/2>
Explanation:
The projection of a vector u onto another vector v is given by;
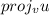 =
=
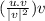 ----------------(i)
----------------(i)
Where;
u.v is the dot product of vectors u and v
|v| is the magnitude of vector v
Given:
u = <-6, -7>
v = <1, 1>
These can be re-written in unit vector notation as;
u = -6i -7j
v = i + j
Now;
Let's find the following
(i) u . v
u . v = (-6i - 7j) . (i + j)
u . v = (-6i) (1i) + (-7j)(1j) [Remember that, i.i = j.j = 1]
u . v = -6 -7 = -13
(ii) |v|
|v| =
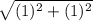
|v| =
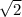
Substitute these values into equation (i) as follows;
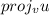 =
=
![[(-13)/((√(2)) ^2)][i + j]](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/mathematics/high-school/9fn1vhe6o4ftcfwjy2mw1ocot40yqib3aj.png)
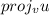 =
=
![(-13)/(2) [i + j]](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/mathematics/high-school/dhvm1wesomykhi1dvlqylursrwnn241a6v.png)
This can be re-written as;
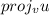 =
=
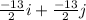
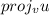 =
=