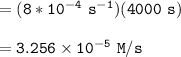Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
From the graphical diagram attached below; we can see the relationship between the concentration of
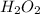 which declines exponentially in relation to the time and it obeys the equation:
which declines exponentially in relation to the time and it obeys the equation:
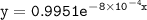
This relates to the 1st order reaction rate, whereby:
The integrated rate law
![\mathtt{ [A] = [A]_o e^(-kt)}](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/chemistry/college/yq5rgdlnqwh9g5n0om84l94msfo4cqrnyd.png)
here:
[A] = reactant concentration at time (t)
[A]_o = initial concentration for the reactant
k = rate constant
As such, the order of the reaction is the first order
Rate constant
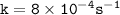
Rate law
![\mathtt{= k[H_2O_2]}](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/chemistry/college/i389vn44syfwz29fzs2by3x30vmihdvnpp.png)
The integrated rate law
![\mathtt{[H_2O_2] = [H_2O_2]_oe^{-(8*10^(-4))t}}](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/chemistry/college/h6bbypv4pjdaad0cztx5qvkn85ivqor945.png)
From the given table:
the initial concentration of
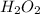 = 1.00 M
= 1.00 M
∴
We can determine the concentration of the reactant at 4000s by using the formula:
![\mathtt{[H_2O_2] = [H_2O_2]_oe^{-8*10^(-4)(t)}}](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/chemistry/college/fb6fhga8vzhoz11cw3egm1yyv4y6s56e49.png)
![\mathtt{[H_2O_2] = (1.00\ M)*e^{-8*10^(-4)(4000)\ s}}](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/chemistry/college/o58kkchsssom8q5h1j8zk0k0nxle0nwk4v.png)
![\mathtt{[H_2O_2] =0.0407 \ M}](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/chemistry/college/3a68r89nj0o8wwsep4hhz5ae59e4qv2ex1.png)
Finally, at 4000s: the average rate is: