Answer:
The kinetic energy and potential energy lost to friction is 2,420 J.
Step-by-step explanation:
Given;
total mass, m = 40 kg
initial velocity of the girl, Vi = 5 m/s
hight of the hill, h = 10 m
length of the hill, L = 100 m
initial kinetic energy of the girl at the top hill:
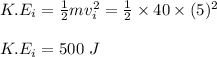
initial potential energy of the girl at the top hill:
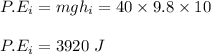
Total energy at the top of the hill:
E = 500 J + 3920 J
E = 4,420 J
At the bottom of the hill:
final velocity = double of the initial velocity = 2 x 5 m/s = 10 m/s
hight of the hill = 0
final kinetic energy of the girl at the bottom of the hill:
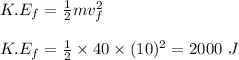
final potential energy of the girl at the bottom of the hill:
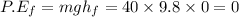
Based on the principle of conservation of energy;
the sum of the energy at the top hill = sum of the energy at the bottom hill
The energy at the bottom hill is less due to energy lost to friction.
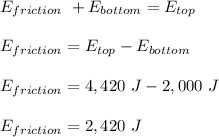
Therefore, the kinetic energy and potential energy lost to friction is 2,420 J.