Answer:
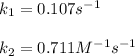
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello there!
In this case, according to the given information and the attached picture in which we can see the units of the rate constant, it turns out possible for us to realize the two called rate laws are:
![r=k[A]\\\\r=k[A]^2](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/chemistry/college/l2lhaj48chliygu5apu4qu8luzdj13sfjs.png)
The former is first-order and the latter second-order; in such a way, we solve for the rate constant in both cases to obtain the following:
![k=(r)/([A])=(1.6x10^(-2)M/s)/(0.15M)=0.107s^(-1) \\\\k=(r)/([A]^2)=(1.6x10^(-2)M/s)/((0.15M)^2)=0.711M^(-1)s^(-1)](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/chemistry/college/wg15di7fpl8mvtkv5bwvozyj2pfw98l9e6.png)
Regards!