Answer:
We have:
R = (2, 2)
S = (5, 4)
RS is the segment that connects R with S.
So RS is just the distance between R and S.
Remember that the distance between two points (a, b) and (c, d) is given by:
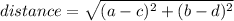
Then the distance between S and R is
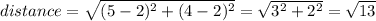
Then:
RS = √13
ii) Now we want to express RS in the form (K, Q)
where K is the magnitude (we already know that it is √13) and Q is the bearing, which is measured with respect to the horizontal axis.
To interpret the bearing, let's look at the image below:
We can use the relation:
Tan(θ) = (opposite cathetus)/(adjacent cathetus)
where the opposite cathetus is just the difference between the y-values:
Opposite cathetus = 4 - 2 = 2
And the adjacent cathetus is the difference between the x-values:
Adjacent cathetus = 5 - 2 = 3
Then we have:
Tan(θ) = 2/3
If we apply the inverse tangent equation to both sides, we get:
Atan(tan(θ)) = Atan(2/3)
θ = Atan(2/3) = 33.69°
The bearing is 33.69°
then:
RS = (√13, 33.69°)