Answer: In the given reactions neither reaction 1 nor 2 reaction leads to an increase in entropy.
Step-by-step explanation:
The degree of randomness present in the molecules of a substance is called entropy.
In gases, molecules are held by weak forces due to which they move apart from each other. Hence, they have high entropy.
In liquids, molecules are a little close to each other so they have less entropy than gases.
In solids, molecules are tightly held together so they have least or negligible entropy.
As reaction 1 is
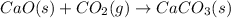 and it shows that product is in solid state. Therefore, entropy is decreasing.
and it shows that product is in solid state. Therefore, entropy is decreasing.
As reaction 2 is
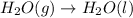 and it shows that gas is converted into liquid. Therefore, entropy is also decreasing here.
and it shows that gas is converted into liquid. Therefore, entropy is also decreasing here.
Thus, we can conclude that in the given reactions neither reaction 1 nor 2 reaction leads to an increase in entropy.