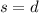Answer:
The distance travelled does not depend on the mass of the vehicle. Therefore,
Step-by-step explanation:
This deceleration situation can be analyzed by means of Work-Energy Theorem, where change in translational kinetic energy is equal to the work done by friction:
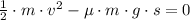 (1)
(1)
Where:
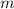 - Mass of the car, in kilogram.
- Mass of the car, in kilogram.
 - Initial velocity, in meters per second.
- Initial velocity, in meters per second.
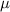 - Coefficient of friction, no unit.
- Coefficient of friction, no unit.
 - Travelled distance, in meters.
- Travelled distance, in meters.
Then we derive an expression for the distance travelled by the vehicle:
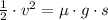
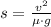
As we notice, the distance travelled does not depend on the mass of the vehicle. Therefore,