Answer:
The answer is below
Step-by-step explanation:
Given that the volume (V) = 0.4 m³, temperature difference (ΔT) = 270 K - 350 K = -80 K, pressure (P) = 60 kPa = 60000 Pa, R = 8.314 J/molK
Since we have constant volume, we can use the final state parameters to calculate the number of moles using the ideal gas law:
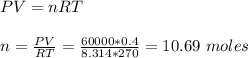
Given that the molar heat capacity at constant volume (
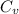 ) = 28.0 J/(mol K), the heat absorbed (Q) is:
) = 28.0 J/(mol K), the heat absorbed (Q) is:
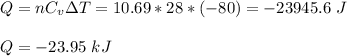
Q ≈ -24 kJ