Answer: The correct option is B.
Step-by-step explanation:
The oxidation reaction is defined as the reaction in which a chemical species loses electrons in a chemical reaction.
A reduction reaction is defined as the reaction in which a chemical species gains electrons in a chemical reaction.
The chemical species will undergo a reduction reaction if the value of standard reduction potential is more positive or less negative.
For the given half-reactions:
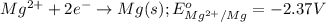
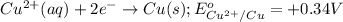
As the value of standard reduction potential of copper is positive thus, it will undergo a reduction reaction and magnesium will undergo an oxidation reaction.
The half-reaction follows:
Oxidation half-reaction:
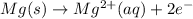
Reduction half-reaction:
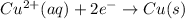
Overall cell-reaction:
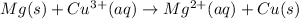
As it can be seen from the reaction that copper is forming as a pure metal in the product thus, it will be deposited and magnesium will be dissolved forming an aqueous solution.
Hence, the correct option is B.